July 1, 2021
Drug Wheel
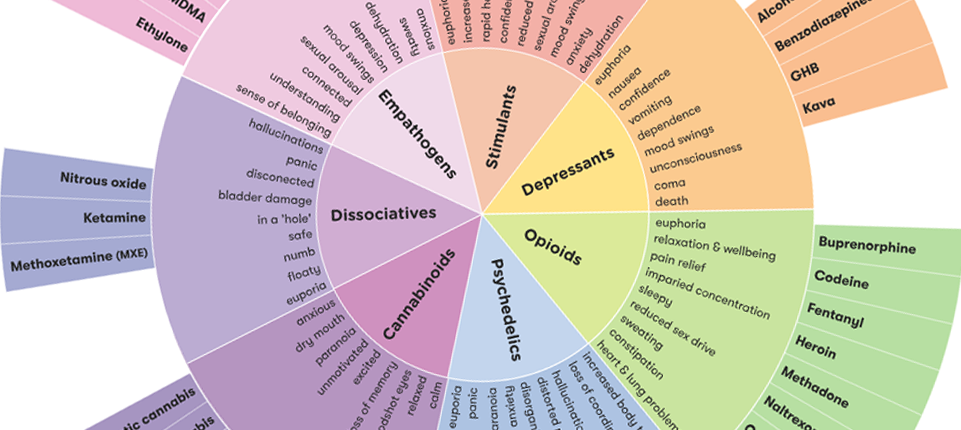
Drugs can be classified in many ways. They can be grouped according to:
- uses (medicinal or recreational)
- effect on the body (the specific effect on the central nervous system)
- source of the substance (synthetic or plant)
- legal status (legal/illegal/decriminalised)
- risk status (dangerous/safe).1
The Drug Wheel is a classification model that groups different types of drugs based on the effect they have on the body. It has seven categories.
Stimulants
Stimulants accelerate messages travelling between the brain and body. They can make a person feel more awake, alert, confident or energetic. They can also cause a person to feel anxious, aggressive or paranoid. Common stimulants include methamphetamine (ice), amphetamines, cocaine, nicotine and caffeine.
Empathogens
Empathogens include substances that cause the brain to release dopamine and serotonin. They can increase feelings of connection and empathy, pleasure and energy levels but can also cause mood swings, dehydration and depression. The most common empathogen is MDMA, or ecstasy.
Psychedelics
Psychedelics are also known as hallucinogens. They can cause hallucinations, or change a person’s thoughts, mood, sense of time or perception of their environment or themselves. Common psychedelics are LSD, peyote and psilocybin.
Dissociatives
Dissociatives are a type of psychedelic drug. They can cause a person to feel disconnected from their body or physical environment. They can also distort physical senses, such as taste, touch, sight, sound and smell. Common dissociatives are ketamine and nitrous oxide.
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids refer to any medicinal, recreational or synthetic substance that joins the cannabinoid receptors of the body and brain. These substances have a similar effect to cannabis, causing a ‘high’ during which a person may feel happy, relaxed, hungry, giggly or quiet and reflective. Cannabis is more commonly known as marijuana.
Depressants
Depressant substances affect the central nervous system, slowing down the messages travelling between the brain and body. Sometimes depressants reduce concentration, inhibitions and coordination and cause people to feel relaxed. Common depressant drugs are alcohol, benzodiazepines, GHB/GBL and inhalants/solvents.
Opioids
Opioids affect the opioid receptors in the brain and are usually derived from the opium poppy. Like depressants, opioids slow the central nervous system and messages travelling between the brain and body. They are often used to treat pain. Common types of opioid include codeine (Panadeine®, Panadeine Forte® and Nurofen Plus®), fentanyl, morphine, methadone, tramadol and heroin.
Frontline health professionals
Drug classifications are applied to different situations. They provide information to help frontline health professionals diagnose and treat different cases such as an overdose.
The Drug Wheel allows paramedics as well as doctors, nurses, healthcare and social workers to quickly understand the effects of different drug types without needing in-depth knowledge of specific or new drugs. This makes it easier to provide treatment, prevent an overdose and develop harm reduction strategies for different types of drugs.
It was first developed in 2011-12, in response to the creation and use of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS). Previously, drugs were categorised as either depressants, stimulants, opioids or hallucinogens, which excluded or mischaracterised some drugs.2
The Alcohol and Drug Foundation was the first organisation in Australia to adopt the classification model.